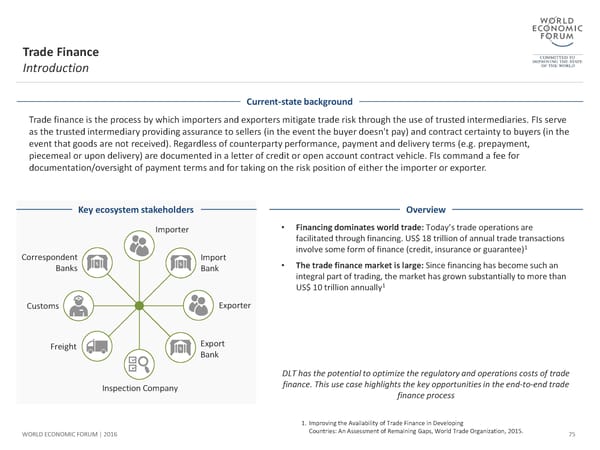
Trade Finance Introduction Current-state background Trade finance is the process by which importers and exporters mitigate trade risk through the use of trusted intermediaries. FIs serve as the trusted intermediary providing assurance to sellers (in the event the buyer doesn't pay) and contract certainty to buyers (in the event that goods are not received). Regardless of counterparty performance, payment and delivery terms (e.g. prepayment, piecemeal or upon delivery) are documented in a letter of credit or open account contract vehicle. FIs command a fee for documentation/oversight of payment terms and for taking on the risk position of either the importer or exporter. Key ecosystem stakeholders Overview Importer • Financing dominates world trade: Today’s trade operations are facilitated through financing. US$ 18 trillion of annual trade transactions involve some form of finance (credit, insurance or guarantee)1 Correspondent Import • The trade finance market is large: Since financing has become such an Banks Bank integral part of trading, the market has grown substantially to more than US$ 10 trillion annually1 Customs Exporter Freight Export Bank DLT has the potential to optimize the regulatory and operations costs of trade Inspection Company finance. This use case highlights the key opportunities in the end-to-end trade finance process 1. Improving the Availability of Trade Finance in Developing WORLD ECONOMIC FORUM | 2016 Countries: An Assessment of Remaining Gaps, World Trade Organization, 2015. 75
 The Future of Financial Infrastructure Page 74 Page 76
The Future of Financial Infrastructure Page 74 Page 76