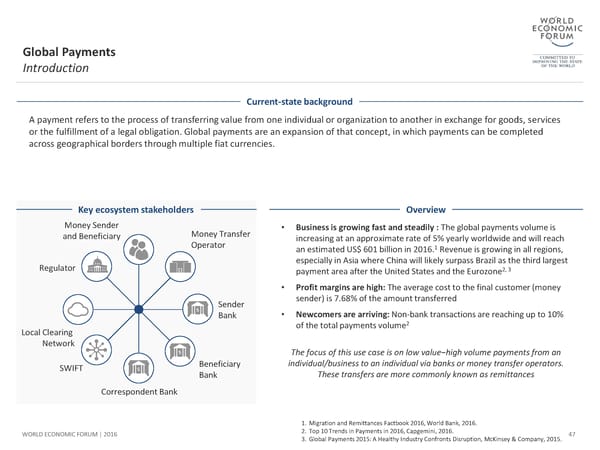
Global Payments Introduction Current-state background A payment refers to the process of transferring value from one individual or organization to another in exchange for goods, services or the fulfillment of a legal obligation. Global payments are an expansion of that concept, in which payments can be completed across geographical borders through multiple fiat currencies. Key ecosystem stakeholders Overview Money Sender Money Transfer • Business is growing fast and steadily : The global payments volume is and Beneficiary Operator increasing at an approximate rate of 5% yearly worldwide and will reach 1 an estimated US$ 601 billion in 2016. Revenue is growing in all regions, Regulator especially in Asia where China will likely surpass Brazil as the third largest payment area after the United States and the Eurozone2, 3 • Profit margins are high: The average cost to the final customer (money Sender sender) is 7.68% of the amount transferred Bank • Newcomers are arriving: Non-bank transactions are reaching up to 10% of the total payments volume2 Local Clearing Network The focus of this use case is on low value−high volume payments from an SWIFT Beneficiary individual/business to an individual via banks or money transfer operators. Bank These transfers are more commonly known as remittances Correspondent Bank 1. Migration and Remittances Factbook 2016, World Bank, 2016. WORLD ECONOMIC FORUM | 2016 2. Top 10 Trends in Payments in 2016, Capgemini, 2016. 47 3. Global Payments 2015: A Healthy Industry Confronts Disruption, McKinsey & Company, 2015.
 The Future of Financial Infrastructure Page 46 Page 48
The Future of Financial Infrastructure Page 46 Page 48